What is Matcha Green Tea?

Matcha green tea stands apart from traditional green tea. It's a vibrant, powdered form with a rich history and numerous potential health benefits. Instead of steeping leaves and discarding them, matcha preparation involves consuming the entire leaf, finely ground into a powder. This method delivers a concentrated dose of nutrients and antioxidants, leading many to wonder about its digestive effects, including whether matcha makes you poop. This unique approach to tea originated centuries ago in Japan, embraced by Zen Buddhist monks for its ability to foster a calm alertness during meditation. To understand these effects, we need to explore what sets matcha apart.
Matcha, like other types of green tea, originates from the Camellia sinensis plant. However, matcha cultivation distinguishes itself through a unique shading process in the final weeks of growth. By limiting sunlight, chlorophyll production increases, resulting in matcha's signature vibrant green color. Furthermore, this shading process elevates the levels of specific amino acids, such as L-theanine, known for its calming properties. These compositional changes influence matcha's interaction with the digestive system, a key factor when exploring its potential laxative properties. In essence, it's the distinct growing and processing methods that truly differentiate matcha from other green teas.
This difference in processing significantly impacts the nutritional profile. Consuming the entire matcha leaf provides a higher concentration of beneficial compounds compared to steeping traditional tea leaves. Matcha is particularly rich in catechins, a type of antioxidant associated with various health benefits. A single serving of matcha delivers a potent dose of antioxidants, exceeding even some well-regarded superfoods. For instance, matcha boasts a considerably higher antioxidant content than spinach or blueberries. Beyond antioxidants, matcha also offers vitamins, minerals, and fiber. These components work together, potentially affecting digestive function and playing a role in matcha's impact on bowel movements. Understanding this composition is crucial for exploring matcha's effect on regularity.
Matcha's Effect on Digestion
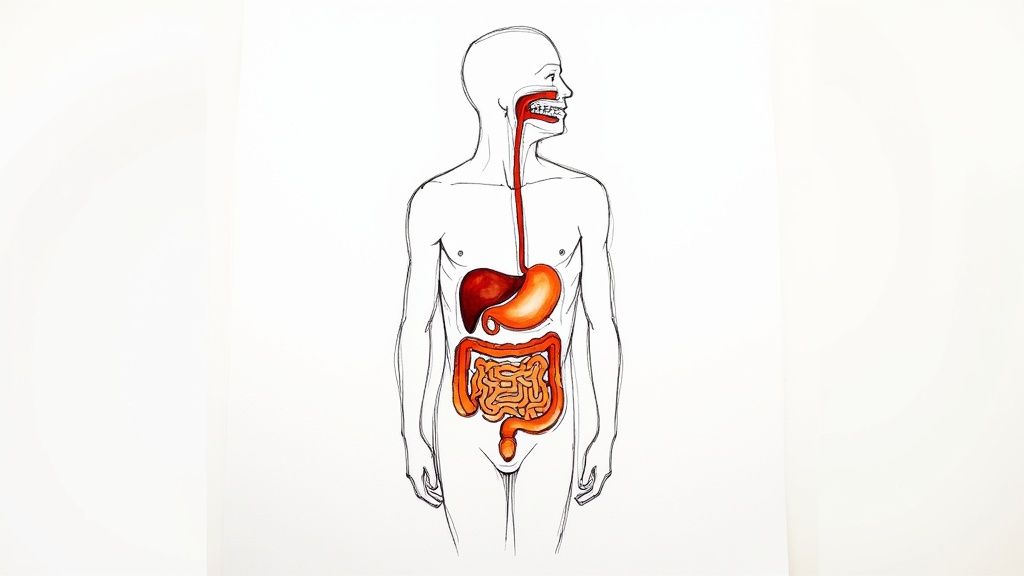
Having explored matcha's unique qualities, let's address a common question: does matcha make you poop? To understand this, we must examine how its components interact with our digestive system. This involves looking beyond immediate effects and considering the overall influence matcha can have on gut health.
Caffeine's Role in Matcha's Digestive Effects
Caffeine is a key factor in matcha's digestive influence. A typical serving of matcha (1-2 teaspoons) contains a moderate amount of caffeine, around 70 milligrams. This caffeine can stimulate the colon, encouraging bowel movements. It acts as a gentle motivator for the digestive system, prompting movement. This explains why some individuals experience a laxative effect after drinking matcha.
The Balancing Act of L-Theanine
Unlike coffee, which often creates a more urgent need for a bathroom break, matcha's caffeine is balanced by L-theanine. This amino acid promotes relaxation and mitigates the sometimes intense effects of caffeine. As a result, while matcha can stimulate bowel movements, it generally does so more gently than coffee. The combination of caffeine and L-theanine creates a more balanced effect on the digestive system.
Beyond Caffeine: Other Digestive Benefits of Matcha
Matcha's potential benefits for digestion extend beyond caffeine. The warmth of the beverage itself can aid digestion. Similar to how a warm bath relaxes muscles, warm matcha can have a soothing effect on the digestive tract, easing its processes. Furthermore, matcha provides a small amount of fiber. While not a significant quantity, this fiber contributes to overall digestive health by adding bulk to stool and promoting regularity. Combined with the hydration from drinking matcha, these factors contribute to a healthier digestive system.
Matcha and Gut Health: A Deeper Look
The question of whether matcha increases bowel frequency is complex. While caffeine can stimulate bowel movements, consistent regularity is more intricate. Research suggests that matcha's impact extends to influencing the gut microbiome. The antioxidants and other compounds in matcha may nourish beneficial gut bacteria while potentially inhibiting harmful ones. This implies that regular matcha consumption may foster a healthier and more balanced gut environment, contributing to overall well-being.
Finding the Right Balance: Matcha Consumption
While matcha may offer digestive benefits, moderation is important. Excessive consumption of any food or beverage, including matcha, can lead to undesirable effects. Too much matcha may cause diarrhea and digestive discomfort due to its caffeine and polyphenol content. For most individuals, one or two cups of matcha per day is a reasonable amount to enjoy its potential benefits without overdoing it. This balanced approach allows you to experience the positive effects on digestion without risking negative consequences.
Caffeine vs L-Theanine Content
We've established that matcha can influence digestion. Now, let's examine the dynamic interplay between two of its key components: caffeine and L-theanine. Understanding this balance is vital to answering the question, "does matcha make you poop?" It's not simply about the presence of caffeine; the interaction with L-theanine plays a crucial role.
Caffeine's Stimulating Effects
Matcha contains caffeine, a known stimulant. A standard serving (1-2 teaspoons) provides roughly 70mg of caffeine. This can stimulate the colon and promote bowel movements, offering a gentle nudge to the digestive system. This stimulating effect explains why some experience increased bowel activity after consuming matcha. Importantly, matcha's caffeine content is lower than coffee's, which typically contains around 95mg per cup. This difference contributes to their contrasting digestive effects.
L-Theanine: The Calming Counterpart
While caffeine stimulates, matcha also contains L-theanine, an amino acid known for its calming properties. This adds nuance to the question of matcha's laxative effects. L-theanine modulates caffeine's effects, working in tandem with it. This means that while matcha can stimulate bowel movements, L-theanine tempers the urgency commonly associated with coffee. The combination is like a smooth accelerator and a gentle brake working together, providing a more balanced experience. This makes matcha's effect on digestion less abrupt and more in sync with the body's natural rhythm.
The Synergy: A Balanced Approach to Digestion
Matcha's unique synergy of caffeine and L-theanine distinguishes it from other caffeinated beverages. This combination stimulates the digestive system without the abrupt, sometimes uncomfortable urgency associated with coffee. Coffee might send you rushing to the restroom, while matcha encourages bowel movements more gently and gradually. This makes matcha a potentially beneficial beverage for supporting healthy digestion. This synergistic interaction is essential to understanding why matcha, despite containing caffeine, doesn't typically elicit the same drastic digestive responses as coffee. It offers a more balanced and harmonious approach to regularity. So, does matcha make you poop? The answer is nuanced, influenced by the interplay of its stimulating and calming components. It's this balance that makes matcha a compelling option for those seeking a gentle approach to digestive support.
Beneficial Compounds in Matcha
From its vibrant green color to its unique preparation, matcha offers a wealth of potential health benefits, thanks to its rich composition. Beyond caffeine and L-theanine, understanding these compounds provides further insight into how matcha interacts with overall digestive health and the question of its laxative effects.
Antioxidants: A Powerhouse of Protection
Matcha is packed with antioxidants, particularly catechins, which are natural plant compounds that protect the body from cellular damage. These antioxidants help combat oxidative stress, a process linked to various health problems. This makes matcha a powerful "superfood," with antioxidants acting like tiny bodyguards, protecting your cells from harmful free radicals.
Catechins: The Star Players
Catechins are the star players in matcha's antioxidant profile. Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), a specific catechin, is particularly abundant and potent. EGCG is associated with a wide range of potential benefits, from supporting heart health to boosting metabolism. This makes matcha an attractive beverage for those seeking to increase their antioxidant intake.
Vitamins and Minerals: Essential Nutrients
In addition to antioxidants, matcha provides essential vitamins and minerals. It's a good source of vitamin C for immune support, along with several B vitamins, crucial for energy production. Matcha also contains minerals like potassium, important for healthy blood pressure, and magnesium, which plays a role in muscle and nerve function. This nutrient profile further enhances matcha's overall health benefits.
Chlorophyll: The Green Pigment
Chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for matcha's vibrant green color, plays a vital role in photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy. While research is ongoing, some studies suggest chlorophyll may offer various human health benefits, including detoxification. This green pigment is more than just aesthetically pleasing; it contributes to matcha's potential health-promoting qualities.
Fiber: Supporting Digestive Health
Matcha contains a small amount of dietary fiber. While not a significant source compared to other foods, this fiber contributes to overall digestive health by adding bulk to stool and aiding regularity. This, combined with the caffeine and L-theanine, helps us further understand how matcha influences bowel movements. So, does matcha make you poop? The combined effects of caffeine, L-theanine, fiber, and warm liquid create a unique synergy that can stimulate bowel movements, though individual responses vary. You might be interested in learning more about matcha's health properties: How to master…. It's important to remember that matcha is not a miracle cure. A balanced diet, adequate hydration, and stress management are all essential for promoting healthy digestion. This holistic approach to gut health is crucial for long-term well-being.
Best Time to Drink Matcha

Having explored the beneficial compounds in matcha and their effects, the question of when to drink it for maximum benefit naturally arises, especially regarding digestion. The timing of your matcha intake can influence how your body processes its components, including its effect on bowel movements. Understanding these nuances can help you integrate matcha effectively into your daily routine.
Morning Matcha: Jumpstarting Your Day and Digestion
Many use matcha as a morning coffee alternative. This can be an excellent choice for supporting regular bowel movements. The caffeine in matcha can stimulate the colon, encouraging a bowel movement soon after consumption. Think of your digestive system as a train track, with morning matcha acting as the conductor, getting things moving. Unlike the jolt of coffee, matcha's L-theanine provides a more balanced energy boost, avoiding a sudden urge to use the bathroom.
Matcha in the Afternoon: A Gentler Boost
Afternoon matcha provides a gentler, sustained energy lift without disrupting sleep. The caffeine and L-theanine combination offers focused, calm alertness. This can be especially helpful for those sensitive to caffeine later in the day. While the digestive effects might be less noticeable than with morning consumption, the warmth and hydration from matcha can still support healthy digestion throughout the day. This is particularly useful for those who experience digestive slowdowns later in the day.
Matcha and Mealtimes: Supporting Digestive Processes
Consider enjoying matcha with meals. The tea's warmth can relax the digestive tract, similar to how warm water can soothe an upset stomach. Additionally, matcha's small amount of fiber adds bulk to stool and supports regularity. This means that drinking matcha with meals can complement your natural digestive processes, enhancing their efficiency and potentially alleviating bloating or discomfort.
Evening Matcha: A Relaxing Ritual (with a Caveat)
While L-theanine's calming effects seem ideal for the evening, the caffeine content could disrupt sleep for some. Avoid matcha close to bedtime if you're caffeine-sensitive. However, if you tolerate caffeine well, a small cup a few hours before bed can be a relaxing ritual. The warmth and calming properties of the tea can promote tranquility before sleep. Remember, individual caffeine responses vary, so listen to your body.
Finding Your Matcha Rhythm
The optimal time to drink matcha depends on your individual needs and preferences. Experiment with different times and observe your body's response, noting energy levels and digestive patterns. Does matcha promote more regular bowel movements in the morning? Does an afternoon cup provide the ideal pick-me-up? Discovering your personal matcha rhythm allows you to maximize its benefits. By attending to your body's unique signals, you can create a matcha routine that supports your overall well-being.
Potential Side Effects
While matcha offers numerous potential health benefits, including digestive support, it's important to be aware of potential side effects, particularly regarding its laxative effects. As with any food or beverage, moderation and awareness are key to responsible consumption. Understanding these potential side effects allows you to make informed choices about your matcha intake.
Caffeine-Related Effects
Matcha contains caffeine, which can be beneficial for some and problematic for others. Although it contains less caffeine than coffee, excessive consumption can still cause problems. Those sensitive to caffeine might experience jitters, anxiety, or difficulty sleeping. Excessive caffeine can also exacerbate underlying heart conditions. Therefore, if you have a heart condition or are sensitive to caffeine, monitor your matcha intake carefully and consider decaffeinated options.
Digestive Issues
While matcha can support healthy digestion, too much can have the opposite effect. Excessive matcha consumption can lead to diarrhea or an upset stomach due to the caffeine and polyphenols. These compounds can overstimulate the digestive tract, causing discomfort. Finding your optimal intake level—the point where matcha supports digestion without adverse effects—is crucial.
Medication Interactions
Matcha can interact with certain medications, potentially interfering with the effectiveness of some antibiotics and anticoagulants. If you are taking medication, consult your doctor or pharmacist before incorporating matcha into your routine. This proactive approach helps avoid potential complications and ensures matcha complements, rather than hinders, your health regimen.
Heavy Metal Contamination
Some matcha products may contain heavy metals like lead, absorbed from the soil during cultivation. While reputable brands adhere to strict quality control measures to minimize this risk, it remains a factor to consider. Choosing certified organic matcha from trusted suppliers can help reduce this risk. Varying your matcha sources is also advisable to prevent potential build-up from a single origin.
Listen to Your Body
The best way to avoid negative side effects is to listen to your body. Start with a small amount of matcha and gradually increase as tolerated. Pay attention to how you feel. Does matcha improve regularity, or does it cause digestive upset? Does it provide sustained energy, or does it make you jittery? By tuning into your body's signals, you can find the right balance and safely enjoy matcha's benefits.
Ready to experience the unique benefits of matcha? Explore our premium selection at matcha-tea.com and discover the perfect blend for your wellness journey!
